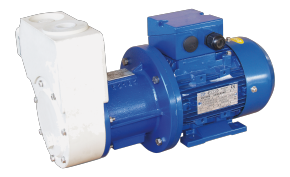
Acids (such as sulphuric, hydrochloric, nitric, phosphoric, hydrofluorosilicic, etc.) are widely used in chemical processing, metal-finishing, electroplating, wastewater treatment, and many other industries. Because acids are aggressive, corrosive, and often hazardous, the equipment used to handle them—especially the pump—must be selected and maintained with care. According to AxFlow, acid-handling requires “acid resistant pumps … tailored to your needs.” axflow.com+2Arroyo Process Equipment+2
The right pump enables safe transfer, minimal downtime, and long service life; the wrong choice brings corrosion, leaks, maintenance issues, and safety risks.
Key Challenges
-
Corrosion of wetted parts: If the pump’s casing, impeller, seals or fasteners aren’t compatible, acid can attack metal or degrade elastomers very quickly. michael-smith-engineers.co.uk+1
-
Material compatibility: Acid concentration, temperature, presence of contaminants or suspended solids can all affect which materials will survive. precisionmachinetech.com+1
-
Seal integrity and leakage risk: Acids demand robust sealing systems—leaks are dangerous. Some pumps use magnetic drives or sealless designs for this. qeehuapump.com+1
-
Viscosity, density and temperature effects: Some acids (e.g., sulphuric) may have high specific gravity or varied viscosities at temperature; these affect system hydraulics and pump selection. axflow.com
-
Safety & environmental risk: The handling of acids often occurs under strict regulatory, safety, and environmental controls. Proper pump selection helps meet these. Thomson Process
Selection & Design Considerations
-
Materials of construction
-
Use materials like stainless steel (316/316L), duplex steel, nickel alloys (Hastelloy), or thermoplastic/fluoropolymers (PVDF, PTFE, PFA) depending on acid type, concentration and temperature. tlpumps.com+2qeehuapump.com+2
-
For heavily corrosive or high-temperature acids, polymer-lined or fully plastic pumps may be required. flowmag.co.uk+1
-
-
Seal technology
-
Mechanical seals designed for acids, or sealless (magnetic drive) pumps to avoid leaks entirely. rotechpumps.com+1
-
Ensure the seal materials (elastomers, faces) are compatible with acid type and conditions.
-
-
Pump type & configuration
-
Centrifugal pumps may be suitable for acid transfer at moderate conditions; positive displacement types may be needed for dosing or viscous acid blends. precisionmachinetech.com
-
Self-priming, lined casings, large clearances if solids or entrained gas present.
-
-
Operating conditions
-
Check temperature, concentration, specific gravity, viscosity, presence of solids, entrained air/gas, suction conditions. michael-smith-engineers.co.uk+1
-
Head and flow requirements must be matched considering acid properties (which may differ from water).
-
-
Safety & ancillary systems
-
Secondary containment for leaks, leak-detection systems, rated materials and coatings, appropriate instrumentation. crestpumps.co.uk
-
Maintenance access and safe procedures: regular inspection, provisions for flushing, neutralising, and cleaning.
-
Best Practice Operation & Maintenance
-
Ensure the pump is filled with the correct prime fluid if required (for non-self-priming types) and that suction inlet is free of air and blockages.
-
Periodically inspect the pump’s wetted parts (casing, impeller, wear rings), seals (packings or mechanical), and fasteners for signs of corrosion or degraded materials.
-
Monitor for changes in flow, pressure, vibration, power consumption — deviations can hint at internal corrosion, leakage, or wear.
-
Flush the system or pump after use if the acid may leave residues, or if working conditions include suspended solids or crystallisation risk.
-
Use correct personal protective equipment (PPE) and safe handling procedures when servicing acid systems — any leak or maintenance operation requires safe isolation and neutralisation.
-
Keep a record of acid concentration, temperature, pump parts/materials, maintenance history — useful for trending and early detection of issues.
Pumping acids is a demanding application that requires specialised pumps, carefully selected materials and rigorous safety and maintenance regimes. By choosing the right construction materials, seal system, and pump type — and operating with vigilance — you safeguard both your equipment and personnel, while achieving reliable, efficient acid transfer.
Because of our wide product range and expertise in the field of fluid transfer, we are able to offer acid pumps for any acid including those with high viscosities and high specific gravities such a sulphuric acid but, also highly corrosive acids such as Nitric Acid and Hydrofluoric acid across the UK and tailored to your needs.
Some of the most common acidic liquids are: Phosphoric Acid, Sulphuric Acid, Hydrochloric Acid, silver nitrate, Citric Acid, Nitric acid, Hydrofluorosilicic acid and CIP fluids.