How to maintain gear pumps
As with any other pump, regular maintenance is vital to reducing costly repairs and maximizing pump efficiency. Below is a guide to operating your gear pump and ensuring it achieves a long operating life through regular maintenance.
By following regular maintenance schedules and adhering to proper operation procedures, gear pumps can be an efficient and productive solution to high-viscosity pumping needs
- Check bearings regularly: The bearings are a key area of gear pumps to maintain due to the imbalance they could potentially create if they are defective. Therefore, it is important to check bearings regularly and replace as necessary by removing the defective bearing. A common indicator of worn bearings may be excessive noise.
- Running dry: Unlubricated gear teeth will create large amounts of friction leading to head heat as the cogs expand and begin rubbing against the housing, which may destroy the pump, and thus leading to costly repair and downtime.
- Fluid viscosity: Gear pumps (primarily internal gear pumps) are designed to handle highly viscous fluids to minimize slip. Pumping low viscosity fluids leads to a reduced flow rate and efficiency as it ‘slips’ through the tight spaces from the higher-pressure discharge side of the pump to the lower-pressure suction side of the pump.
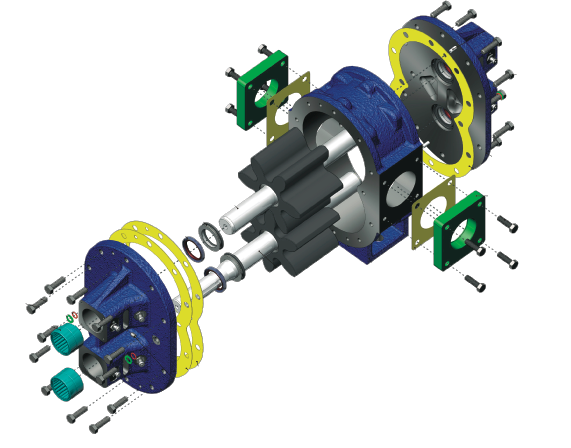
A gear pump’s toothed gear construction allows particles to become trapped in small spaces, accelerating wear and reducing efficiency. If you need to transfer fluid containing abrasives, consider contacting the pump manufacturer to discuss hardened material options.
Gear pumps require good installation, a PRV to protect the pump from overpressure and an assured supply of clean liquid. Gear pumps that have outboard bearings need the bearings to be lubricated. Mechanical seals come with their own set of problems. If mechanical seals are fitted it becomes critical that shafts run true and the process pressures and flows are steady and do not vary largely to load up the bearings and gear teeth unevenly.