How to maintain axial flow pumps
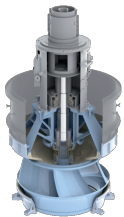
Axial flow pumps—also known as propeller pumps—are designed for high-flow, low-head applications such as flood control, cooling water circulation, and large-scale water transfer.
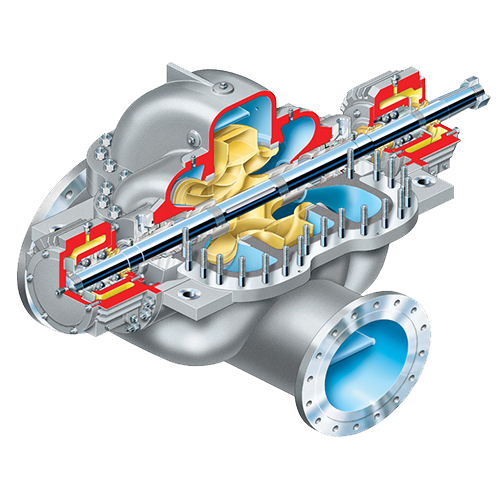
These pumps are robust and efficient but operate under demanding hydraulic conditions. To ensure long service life and optimal efficiency, they require regular maintenance and condition monitoring of key components such as impellers, shafts, bearings, and seals.
Routine Inspection and Monitoring
Visual and Operational Checks
-
Inspect for leaks around stuffing boxes, mechanical seals, and column pipe joints.
-
Monitor vibration and noise: Unusual vibration may indicate imbalance, misalignment, or bearing wear.
-
Record discharge pressure, flow rate, and power consumption: Variations may signal impeller wear or obstructions.
-
Check bearing temperatures: Overheating suggests inadequate lubrication or bearing fatigue.
Performance Tracking
-
Maintain a log of pump performance (flow, head, and current draw).
-
Compare with factory test data or previous readings to identify declining efficiency or early wear.
Lubrication and Bearings
-
Line Shaft Bearings:
-
May be either water-lubricated or oil-lubricated depending on design.
-
Ensure a clean, continuous supply of lubricant to prevent metal-to-metal contact.
-
For water-lubricated bearings, verify flow and cleanliness of the flush water.
-
-
Thrust Bearings (at the discharge head):
-
Check for proper oil level and cleanliness.
-
Replace or filter oil if contamination is detected.
-
Monitor bearing temperature and vibration; rising levels indicate wear or misalignment.
-
-
Regular lubrication schedule: Follow manufacturer intervals, adjusting for operating hours and environmental conditions.
Shaft and Coupling Alignment
-
Axial flow pumps often operate in vertical configurations, so correct shaft alignment is critical.
-
Misalignment causes vibration, premature bearing wear, and seal leakage.
-
After installation, overhaul, or temperature changes, re-check alignment between the pump shaft and motor drive.
-
Inspect flexible couplings for cracks or wear; replace coupling inserts as required.
Impeller and Column Maintenance
-
Inspect impeller blades for erosion, corrosion, cavitation, or buildup of solids.
-
Clean and polish minor deposits; replace or recondition blades showing heavy pitting or distortion.
-
Check blade pitch angle (if adjustable) for uniformity and correct setting per design duty.
-
Inspect column bearings, shaft sleeves, and wear rings for scoring or abrasion.
-
Ensure internal clearances remain within manufacturer tolerances to prevent vibration and flow losses.
Mechanical Seals and Packing
-
Inspect mechanical seals for leakage and wear; replace seal faces or elastomers if leakage exceeds acceptable limits.
-
For packed glands, maintain slight, controlled leakage for lubrication.
-
Use seal materials compatible with pumped fluid and temperature.
-
Check seal flush or cooling lines for blockages or contamination.
Suction and Discharge Systems
-
Keep suction screens and strainers clean to prevent clogging and cavitation.
-
Inspect suction bells for debris, corrosion, or damage to guide vanes.
-
Ensure discharge valves, bends, and expansion joints are secure and properly supported to avoid vibration transfer.
-
Verify that suction submergence is adequate under all operating conditions to prevent air entrainment.
Scheduled Overhaul
-
Perform a comprehensive inspection every 6–12 months, depending on service conditions.
-
Disassemble and clean impellers, columns, and bearings.
-
Measure shaft straightness and impeller runout.
-
Replace worn wear rings, bearings, and seals.
-
Check for corrosion or fatigue cracks in welded joints.
-
-
After reassembly, re-align the shaft and perform a performance test before returning the pump to service.
Storage and Preservation
When pumps are out of service for extended periods:
-
Drain and dry all internal passages to prevent corrosion.
-
Coat metallic surfaces with a rust-preventive oil or protective film.
-
Store the pump in a clean, dry, vibration-free environment.
-
Rotate the shaft periodically to prevent bearing brinelling and sticking
For information on our pump repair services click here.